Metals and non-metals
Aims of this page
After studying this page, you should be able to:
- locate metal and non-metals on the periodic table
- describe typical properties of metals and non-metals
- explain how an element’s reactions are related to the electronic configuration of its atoms.
Positions in the periodic table
In general, you find metals on the left-hand side of the periodic table and non-metals on the right-hand side. Notice that:
- there are 118 known elements
- there are many more metals than non-metals.
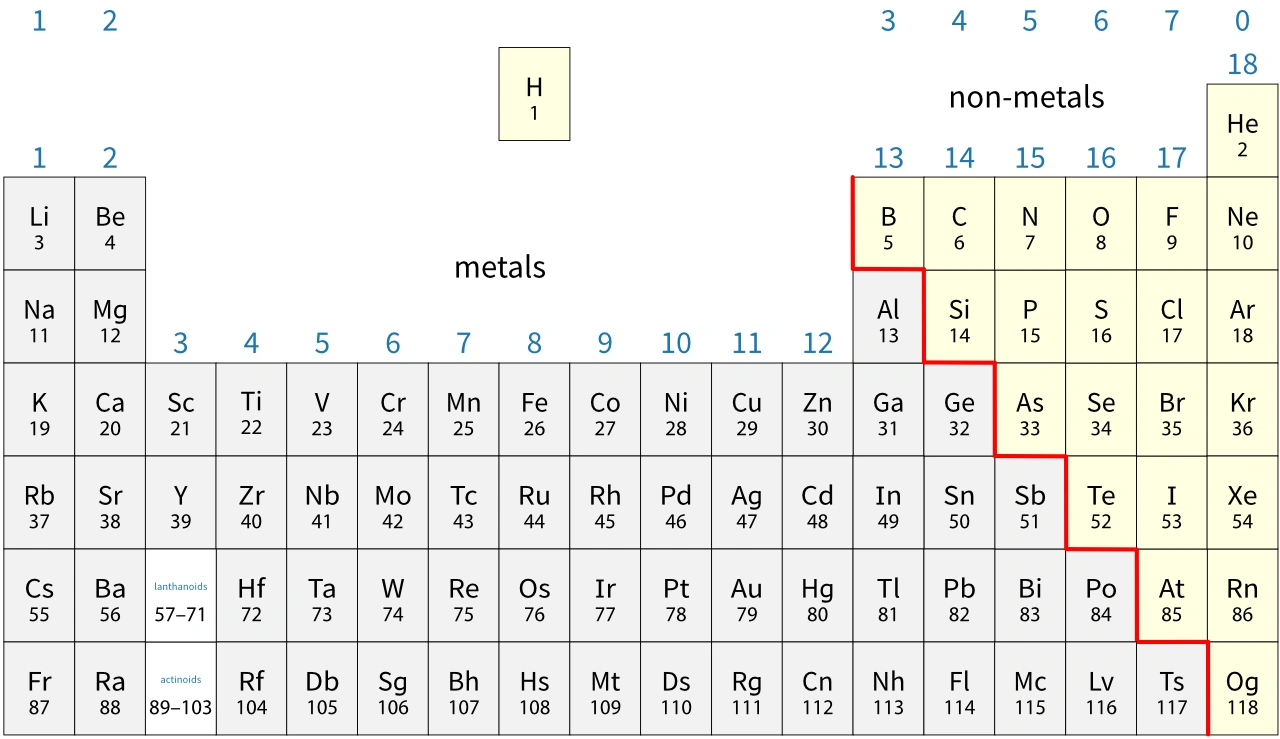
- boron, B
- silicon, Si
- germanium, Ge
- arsenic, As
- antimony, Sb
- tellurium, Te
- polonium, Po
- astatine, At
Tennessine (Ts) may be a metalloid, but very little is known about its properties.
Properties
A property is a feature of something that can be measured or observed:
- physical properties are measured using devices such as thermometers
- chemical properties are determined by observing chemical reactions.
The typical properties of metals and non-metals are different.
Physical properties
The table summarises some typical physical properties of metals and non-metals.
| Physical property | Metals | Non-metals |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point and boiling point | High | Low |
| Appearance when solid | Shiny | Dull |
| Density at rtp (room temperature and pressure) | High | Low |
| Electrical conductivity | Good | Poor |
| Thermal conductivity | Good | Poor |
| Response to external forces when solid | Malleable and ductile | Brittle |

Remember that these are typical properties. Some metals and non-metals have different properties to these. For example:
- mercury is a metal in the liquid state at room temperature
- carbon is a non-metal in the solid state at room temperature
- graphite (a form of carbon) is a good conductor of electricity
- diamond (a form of carbon) is a good conductor of thermal energy.
Properties
A property is a feature of something that can be measured or observed:
- physical properties are measured using devices such as thermometers
- chemical properties are determined by observing chemical reactions.
The typical properties of metal and non-metal elements are different.

Physical properties
The table summarises some typical physical properties of metals and non-metals.
| Physical property | Metals | Non-metals |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point and boiling point | High | Low |
| Appearance when solid | Shiny | Dull |
| Density at rtp (room temperature and pressure) | High | Low |
| Electrical conductivity | Good | Poor |
| Thermal conductivity | Good | Poor |
| Response to external forces when solid | Malleable and ductile | Brittle |
Remember that these are typical properties. Some metals and non-metals have different properties to these. For example:
- mercury is a metal in the liquid state at room temperature
- carbon is a non-metal in the solid state at room temperature
- graphite (a form of carbon) is a good conductor of electricity
- diamond (a form of carbon) is a good conductor of thermal energy.
Chemical properties
The table summarises some typical chemical properties of metals and non-metals.
| Chemical property | Metals | Non-metals |
|---|---|---|
| Bonding between atoms | Metallic | Covalent |
| Reactions with metals | None - mixtures (alloys) form | Ionic compounds form |
| Reactions with non-metals | Ionic compounds form | Simple molecules or giant covalent structures form |
| Ions formed in reactions and during electrolysis | Positively charged (cations) | Negatively charged (anions) |
| Oxides | Basic (soluble oxides form alkaline solutions) React with acids | Acidic React with bases |
Remember that these are typical properties. Some metals and non-metals have different properties to these. For example:
- gold, platinum and other ‘precious metals’ are very unreactive metals
- helium and the other noble gases are very unreactive non-metals that do not readily form compounds.
Worked example 1
Silica, SiO2, is in the solid state at room temperature. Predict three properties of this compound. Explain your answer.Silica is likely to have a giant covalent structure. It should have acidic properties and be able to react with bases.
This is because silica is a compound of two non-metals, silicon and oxygen. These compounds have covalent bonding, and covalent substances in the solid state usually have a giant structure. The oxides of non-metals are acidic and react with bases.

Links with electronic configurations
Chemical reactions involve atoms losing, gaining or sharing electrons. The more easily this happens, the more reactive an element is.
Metals
Metal atoms lose electrons when they react with non-metals. They form positively charged ions when they do this. The table summarises the link between a metal’s position in the periodic table and the ions it forms in reactions.
In general, group 1 metals are more reactive than group 2 metals, and these are more reactive than group 3 metals. Also, metals become more reactive as you go down a group. This means that the most reactive metals are found towards the bottom left of the periodic table.
However …
… the transition elements (the large block of metals between groups 2 and 3) are relatively unreactive compared to other metals. They include:
- metals such as gold and platinum, which are used to make jewellery because they stay shiny
- metals such as copper and silver that react only slowly with other substances.
Worked example 2
Suggest a reason why iron, Fe, is less reactive than potassium, K. Give your answer in terms of the positions of these two metals on the periodic table.
Potassium is in the middle of group 1, which contains very reactive metals. Iron is a transition element, and these are relatively unreactive.

Non-metals
Non-metal atoms gain electrons when they react with metals. They form negatively charged ions when they do this. The table summarises the link between a non-metal’s position in the periodic table and the ions it forms in reactions.
In general, group 7 non-metals are more reactive than group 6 non-metals, and these are more reactive than group 5 non-metals. Also, non-metals become more reactive as you go up a group. This means that the most reactive non-metals are found towards the top right of the periodic table.
However …
… the atoms of elements in group 0 (group 18) have full outer shells. This means that they have no tendency to lose, gain or share electrons. Group 0 elements are very unreactive because of this.
